In Vitro Genetic Toxicology Assays
Inotiv offers a variety of in vitro assays
to meet your regulatory needs.

In Vitro Micronucleus Assay (OECD 487) and
Chromosome Aberration Assay (OECD 473)
In Vitro Micronucleus Assay Options:
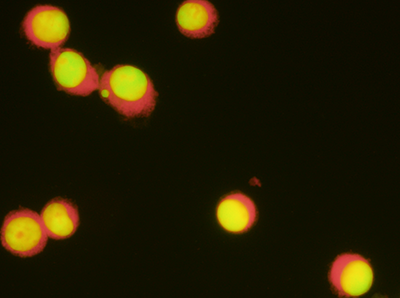
At Inotiv, we leverage the in vitro micronucleus (MN) test as a vital part of our genotoxicity assessments. This essential assay provides critical insights into a test substance's potential to damage genetic material in cells that have completed at least one cell division cycle during or following test substance exposure. This methodology ensures the comprehensive detection of both aneugens (substances leading to abnormal chromosome counts) and clastogens (substances inducing chromosomal breakage or disruption). Studies are performed with (+S9) and without (-S9) metabolic activation and include measurement of cytotoxicity by various methods (population doubling, cytokinesis blocked proliferation index (CBPI) or Relative Viability Cell Count (RVCC), Relative Viability Cell Count (RICC), dependent on the cell type utilized.

The cell lines currently offered at Inotiv for the in vitro MN assay are:
- TK6 cells of human origin
- Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes (HPBL)
- CHO-WBL
- CHO-K1
- A375
- Human-derived epidermal keratinocytes reconstructed skin model (EpiDermTM)
Analysis for micronuclei is performed either by florescence microscopy or via flow cytometry.
All of our in vitro MN assays can be performed to follow the GLP regulations or as a non-GLP test for screening purposes.
Mode of Action (MOA) Determination for In Vitro Micronucleus: FISH and CREST
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) probes and CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, esophageal dysfunction, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) antibody labeling technologies investigate the mode of action for a test substance that is positive in an in vitro micronucleus assay. The FISH and CREST labeling identify whether a micronucleus contains a whole chromosome(s), as a result of an aneugenic mechanism, or a chromosome fragment(s) as a result of a clastogenic mechanism. An aneugenic mechanism may be useful in identifying a threshold, which is very important in the overall risk assessment of a compound. The micronucleus assay with FISH or CREST is ideal for use as a follow up assay to explore mode of action (aneugenic or clastogenic) from an initial genotoxicity result.
Chromosome Aberration Test Options:
Another assay that is of importance in identifying substances that can damage genetic material is the chromosome aberration test. The chromosome aberration assay measures structural abnormalities in chromosomes in vitro.
A structural aberration can directly break DNA strands or disrupt normal DNA replication processes, leading to DNA breaks. These breaks can manifest as deletions, insertions, or rearrangements of chromosome sections. If these DNA breaks are not repaired, or are repaired incorrectly, could lead an increased risk of cancer.
Chromosome aberration tests are performed with (+S9) and without (-S9) metabolic activation and includes measurement of cytotoxicity either by mitotic inhibition or cell growth inhibition (utilizing relative increase in cell counts). The analysis of chromosomal abnormalities is performed on metaphase spreads.
The cell lines currently offered at Inotiv for the in vitro chromosome aberration assays are:
- Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes
- CHO-WBL
- CHO-K1
All of our chromosome aberration assays can be performed to follow the GLP regulations or as a non-GLP test for screening purposes.
In Vitro FAQ:
Difference between chromosome aberration and in vitro micronucleus?
The chromosome aberration assay provides more comprehensive and qualitative information regarding the structural damage (breaks, gaps, interchanges between chromatid and chromosome) and high-level information on numerical changes (endo-reduplication, centromeric split, polyploidy) in chromosomes. The in vitro micronucleus assay provides quantitative damage in terms of micronucleus induction. A follow up test using either FISH or CREST is required to understand the mechanism of micronucleus formation (aneugen vs clastogens).
Which cell lines are preferred to use for in vitro assays?
HPBL in vitro micronucleus assay, HPBL chromosome aberration assay, and TK6 in vitro micronucleus assay should be preferred over the rodent based cell lines (CHO-WBL, CHO-K1, V79, CHL cells) since they are human based test systems with functional p53 genes.
Microscopic vs flow cytometry analysis?
Both modalities are valid and acceptable methods of analysis. Microscopic analysis of in vitro micronucleus or chromosome aberrations is quantitative data based on expert visual observation of the slides that allows the confirmatory review of specimens on slides as needed. Flow cytometer based in vitro micronucleus evaluation is performed using larger sample sizes and provides quick, reliable, and reproducible objective data using validated flow cytometers.
When to use FISH/CREST?
When micronucleus induction is positive in either microscopy or flow cytometry, a mechanistic in vitro micronucleus study using FISH or CREST analysis is recommended to be performed for risk assessment to identify Mode of Action.
Explore other genetic toxicology assays:
| Mutation | Cytogenetic Damage | DNA Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Ames assay | In Vitro Micronucleus assay | Comet assay |
| HPRT assay | Chromosome Aberration assay | |
| Mouse Lymphoma assay | In Vivo Micronucleus assay | |
| Pig-a assay |


_%20As%20a%20Potential%20_i_In%20Vitro__i_%20Micronucleus%20Ass.jpg?width=150&height=90&name=Inotiv%20Resource%20Content%20Thumbnails_0021_Human%20Melanoma%20Cell%20line%20(A375)_%20As%20a%20Potential%20_i_In%20Vitro__i_%20Micronucleus%20Ass.jpg)

