Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK) Solutions

At Inotiv, our comprehensive Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK) capabilities are built on a foundation of personalized study design, quick turnaround, and unparalleled expertise. We understand the unique challenges and varying needs of our clients in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Benefit from our world-class team of scientists and 40+ year track record of providing leading pharma and biotech companies with attentive, decisive analytical services yielding high-quality data.
Our tailored drug discovery packages, designed to suit each stage of development, equip you with the necessary solutions and insights for making well-informed decisions.
To talk to an expert about our DMPK services, please click here.

Direct Scientific Engagement
Bridging Bench Science with Clinical Development
Inotiv's collaborative drug metabolism and DDI study de-risks small molecule candidates by translating advanced assays (like CYP inhibition and targeted proteomics) into actionable insights for our customers. This work directly supports regulatory IND-enabling packages, informs DDI risk assessments, and guides clinical development strategies, ensuring a smoother transition from discovery to the clinic.
Click the image to download our white paper!
Capabilities Flyers
Inotiv Standard IND-Enabling In Vitro DMPK Package for Small Molecules
Accelerate your drug development with Inotiv's tailored in vitro DMPK package. Our team of experienced scientists leverages state-of-the-art facilities and proven methodologies to deliver accurate and reliable data. From bioanalytical method development to excretion studies, we provide a comprehensive suite of customizable services to support your drug discovery and development goals.
Click the image to download our capabilities flyer!
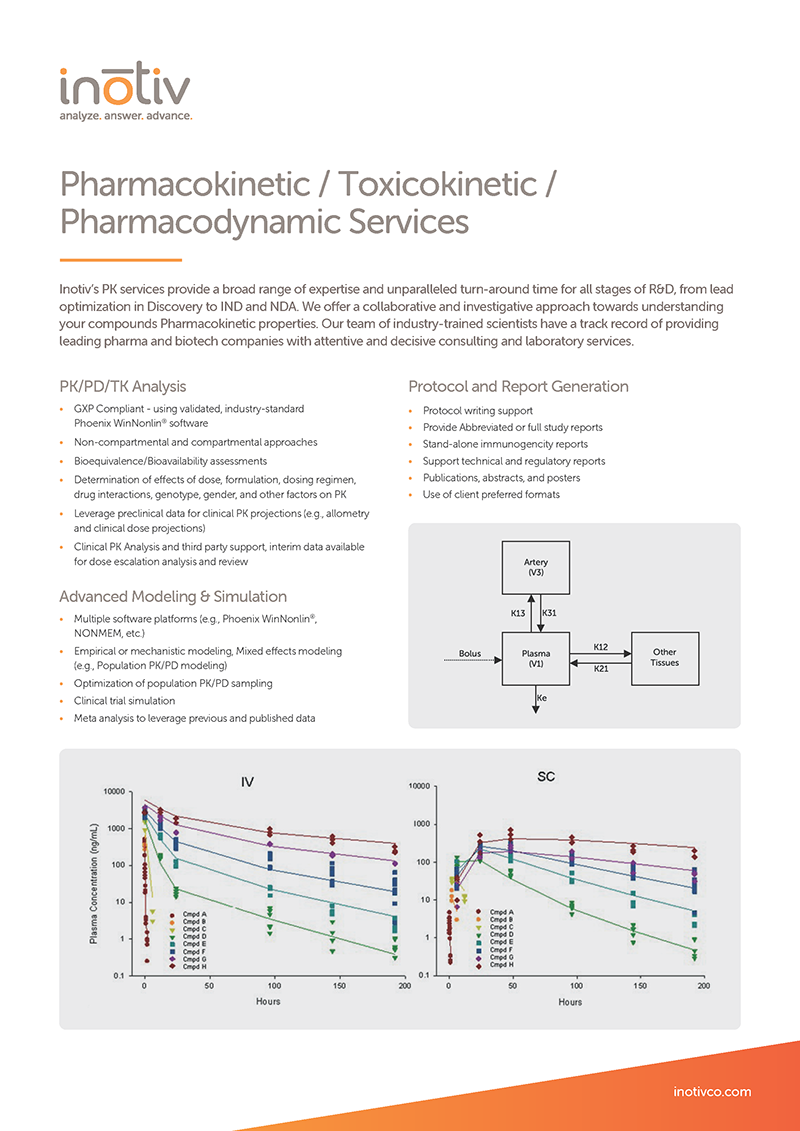
Pharmacokinetics, Toxicokinetics, and Modeling Insights For Your Data
Whatever the source of your data, we will perform PK-TK analyses to evaluate dose, DDI potential, bioequivalence/bioavailability, and/or clinical PK projections.
You benefit from:
- Discovery through regulated PK/TK analyses
- IND enabling report preparation (nonclinical pharmacology summary)
- Exposure-effect modeling (PK/PD)
- Nonclinical pharmacokinetic modeling (pharmacology and toxicology dose design)
- Phoenix™ WinNonlin™ validated software
- Watson LIMS™ noncompartmental PK analysis (NCA)
- Human PK predictions and dose projections (allometric, single species scaling)
- Internal and external consultants with diverse PK, PK/PD modeling experience
Click the image to download our capabilities flyer!
Scientific Posters
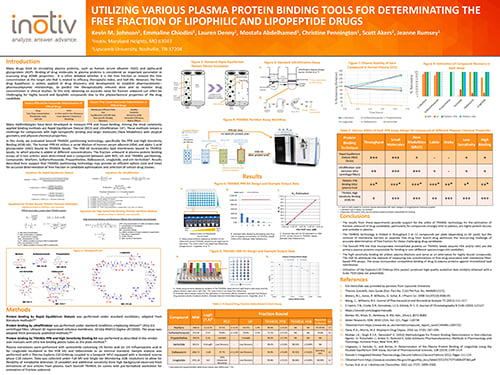
Utilizing Various Plasma Protein Binding Tools for Determinating
the Free Fraction of Lipophilic and Lipopeptide Drugs
Plasma protein binding plays a pivotal role in drug development, serving as a critical parameter for assessing the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) of potential therapeutic compounds. Understanding the degree of plasma protein binding is essential as it directly influences a drug's ADME & DMPK properties such as distribution, bioavailability, and efficacy. Drugs that exhibit high protein binding tend to have a reduced rate of distribution to target tissues and a longer half-life, potentially necessitating lower dosages for therapeutic effect. Conversely, drugs with low protein binding may have a rapid distribution and clearance, requiring higher doses.
Click the image to download our scientific poster!
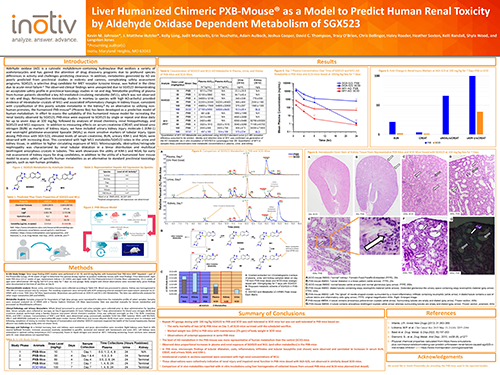
Liver Humanized Chimeric PXB-Mouse® as a Model to Predict Human Renal
Toxicity by Aldehyde Oxidase Dependent Metabolism of SGX523
This work showcases the utility of KIM-1 and NGAL for early risk assessment of kidney injury of drug candidates, in addition to the utility of a humanized liver mouse models to assess safety concerns and predict human metabolites as an alternative to standard preclinical toxicology species such as non-human primates.
Click the image to download our scientific poster!
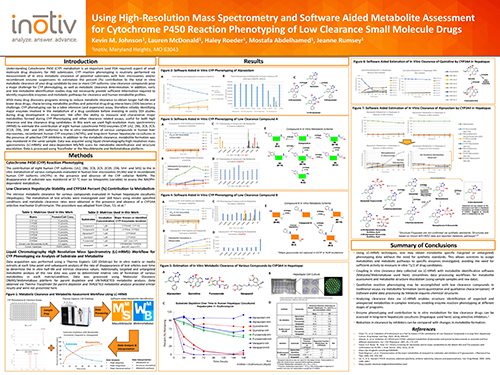
Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Software
Aided Metabolite Assessment for Cytochrome P450 Reaction
Phenotyping of Low Clearance Small Molecule Drugs
Analysis of metabolites formed in reaction phenotyping assays for low clearance compounds provides additional sensitivity for estimating CYP contribution to drug metabolism. Combining High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and software-aided metabolite assessment provides a more efficient and informative approach for enzyme phenotyping of drug metabolizing enzymes. This approach may be incorporated when using either recombinant enzymes, subcellular fractions, suspended hepatocytes, and long-term hepatocyte co-cultures.
Click the image to download our scientific poster!
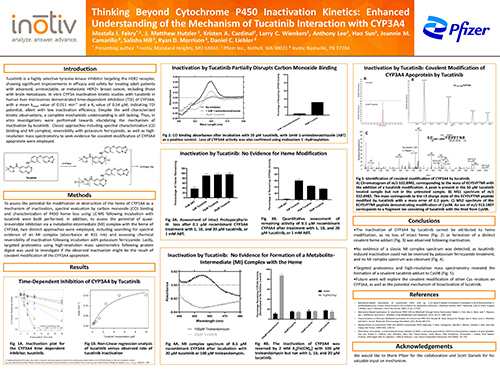
Thinking Beyond Cytochrome P450 Inactivation Kinetics Enhanced Understanding of the Mechanism of Tucatinib Interaction with CYP3A4
Tucatinib has shown significant efficacy in treating advanced HER2+ breast cancer, including cases with brain metastases. In vitro studies identified time-dependent inhibition (TDI) of CYP3A4 by tucatinib, though with low inactivation efficiency. This poster highlights the mechanism behind tucatinib’s interaction with CYP3A4.
Click the image to download our scientific poster!
A Multi-Endpoint Assay Utilizing the All-Human Hepatocyte Tri-Culture Model Truvivo® for Analysis of Hepatic Clearance and Hepatotoxicity Profiles
At the 14th International ISSX Meeting in Chicago, we unveiled compelling new data for the TruVivo® all-human hepatocyte co-culture model. This research, presented by Kevin Johnson, details how the TruVivo system is going beyond conventional in vitro assays. In addition to delivering robust results for metabolic clearance and metabolite ID, the data demonstrates its remarkable ability to distinguish the hepatotoxicity of closely related drugs. This level of precision accelerates drug development by providing highly human-relevant safety insights.
Click the image to download our scientific poster!
Webinars

Download our webinar, DMPK and PD at Inotiv—Moving at the Speed of Discovery, for valuable insight into Inotiv's capabilities within drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics (DMPK).
Featured speakers include Inotiv's industry experts Roger Melton, Vice President of Laboratory Sciences (left), and Jeanne Rumsey, Senior Principal Scientist for DMPK and Biotransformation Lead (right).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK)
What is DMPK?
Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK) is a field in pharmacology and toxicology that focuses on how drugs and foreign substances are processed in the human body. It involves biotransformation, which is the process of metabolically transforming a drug or chemical compound.
What is biotransformation in a pharmacology setting?
Biotransformation: It refers to the modification or transformation of a drug or foreign substance within the body. Enzymes, especially in the liver, carry out this process, converting the original compound into various metabolites. Biotransformation alters the chemical structure, making it more water-soluble and aiding its elimination from the body.
Phases of Biotransformation:
Phase I Metabolism: In this phase, enzymes like cytochrome P450 catalyze reactions like oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis. These reactions introduce or expose functional groups on the drug molecule, making it more amenable to further modification.
Phase II Metabolism: Phase II reactions involve the conjugation of the drug or its Phase I metabolites with endogenous molecules like glucuronic acid, sulfate, glutathione, or amino acids. This conjugation makes the molecules more water-soluble, facilitating their excretion through urine or bile.
What is pharmacokinetics (PK)?
Absorption: PK examines how a drug is absorbed into the bloodstream, considering factors such as the route of administration, chemical properties, and interactions with the gastrointestinal tract.
Distribution: After absorption, PK studies how the drug is distributed throughout the body, considering factors like tissue permeability and blood flow.
Metabolism: Biotransformation is crucial in PK as it determines how a drug is metabolized in the body. Understanding the enzymes involved and the potential formation of active or toxic metabolites is essential.
Excretion: PK assesses how a drug is eliminated from the body, often through the liver, kidneys, or other routes. The rate of excretion determines the drug's half-life and dosing schedules.
What is toxicokinetics?
DMPK is significant in toxicology, helping toxicologists understand the toxicokinetics of chemicals or drugs. This involves studying how toxic substances are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body, with the focus on determining exposure levels that may lead to adverse effects.
Inotiv offers cell and molecular biology services, including gene expression and biomarker analysis, cell-based assays, and protein characterization. Our cutting-edge technology helps validate drug targets and assess therapeutic effects, providing high-quality data and tailored solutions.